What is a DSL Splitter and What Does it Do?
I’m often asked, when arranging Skyway West DSL provisioning, what is a POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) Splitter, and what does it do? DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) technology allows the use of more bandwidth over a customer’s existing copper telephone line for the transmission of data. Basically, the splitter separates voice, which uses a very small proportion of the bandwidth on a line, from the data traffic.
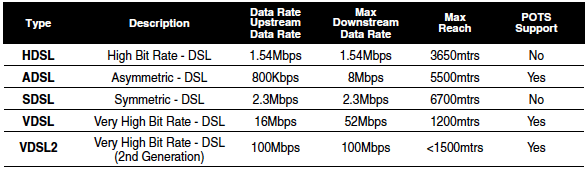
There are a few varieties of DSL technology (see table below) which have key differences to suit different users:
For those varieties of DSL that are supported by POTS, how do we ensure that the data doesn’t interfere with the POTS? As Ronan Kelly of Pulse Engineering describes it:
The main purpose of the DSL over POTS splitter, is to separate the transmission of POTS signals and DSL signals, which enables the simultaneous transmission of both voice and data on the same twisted pair i.e. the POTS + DSL line. The splitter also provides isolation to the POTS signal from interference from DSL signals. Its also provides isolation for the DSL transmission to the POTS from transients generated during POTS signalling (i.e. dialling, ringing, ring trip, off-hook, on-hook etc.).
When DSL and PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) operate on the same line, the electronics inside a normal phone can be a problem for the high frequency DSL signal: the DSL signal can be attenuated (high capacitance on the telephone input, possible resonances inside the telephone, impedance mismatching) and DSL signals can be heard as noise on some phones (phone electronics demodulates high frequency signal outside its operating range to voice frequency noise). In order to keep these systems apart and stop them from interfering with each other it’s necessary to separate the two components from the telephone line.
The DSL POTS Splitter/filter allows full advantage of the bandwidth of the copper line frequency spectrum to be taken, by stopping the telephone and DSL systems from interfering with each other.
The signal from the telephone output is generally just low-pass filtered so that voice frequencies (frequencies up to 3.4KHz, some say 4KHz) pass through without any issues, but higher frequencies are filtered. This filtering generally consists of an LC (L=Inductance, C=Capacitance) low-pass filter designed to some suitable operating frequency between 4 and 20 KHz (between voice and DSL bands). This kind of filter causes the high frequencies of the DSL signal to be severely attenuated (usually by at least 30dB with a good filter) so the signal reaching your telephone equipment does not contain such an amount of high frequency signals that could cause noise.
A vDSL POTS Splitter is a passive low-pass filter designed to provide POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) service in concert with vDSL2 technology. The device blocks high frequency (20kHz-30MHz) energy from interfering with voice equipment and prevents POTS noise from causing data errors on the xDSL connection. They are backwards compatible with all xDSL systems, and result in the best data and voice performance when the DSL router and the telephone are used on the same telephone line.
It’s easily mounted inside the customer premises where the phone service enters the building. Two types of connection options are available: a screw-type terminal block, and standard RJ jacks. This allows the installer to simply connect the existing premise wiring to the PHONE connector or RJ jack on the splitter, and have POTS service up and running within minutes without expensive and time-consuming rewiring.
Skyway West has expertise in all Internet Access Technologies, as well as Network Solutions such as Failover, which can combine ADSL and Cable for the best of both:
Skyway West | Enterprise Level Cable | High Speed Business ADSL